As an engineer at Full Stack Energy, my focus is always on identifying and implementing effective technologies that deliver tangible value to our clients, particularly those committed to pioneering sustainable practices. Our recent work on Real Time Location Services (RTLS) with a customer in the modular office partition sector has brought two advanced Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) positioning technologies into focus: Bluetooth Channel Sounding and Angle of Arrival (AoA) using Constant Tone Extension (CTE). This customer's drive for a circular economy model isn't just a corporate social responsibility initiative; it's a strategic necessity, increasingly shaped by the evolving regulatory landscape here in the EU.
The Regulatory Landscape: Digital Product Passports
In the EU, the push for a circular economy is significantly impacting the construction sector. A key development is the introduction of Digital Product Passports (DPPs) under the revised Construction Products Regulation. These DPPs, soon to be mandatory for many construction products, will contain vital data on a product's origin, composition, and potential for reuse or recycling. While the EU mandates the content and digital accessibility of these passports, it does not specify the underlying physical identification method. Our application addresses this by associating the comprehensive material metadata, which forms the backbone of the Digital Product Passport, with each physical component via its unique Bluetooth LE tag ID. This makes comprehensive tracking with a metadata database an essential tool for compliance and efficient lifecycle management of components like office partitions.
This brings us to how advanced BLE positioning technologies can support this future. Let's explore how Channel Sounding and CTE-based AoA can assist in managing the lifecycle of their valuable office partitions.
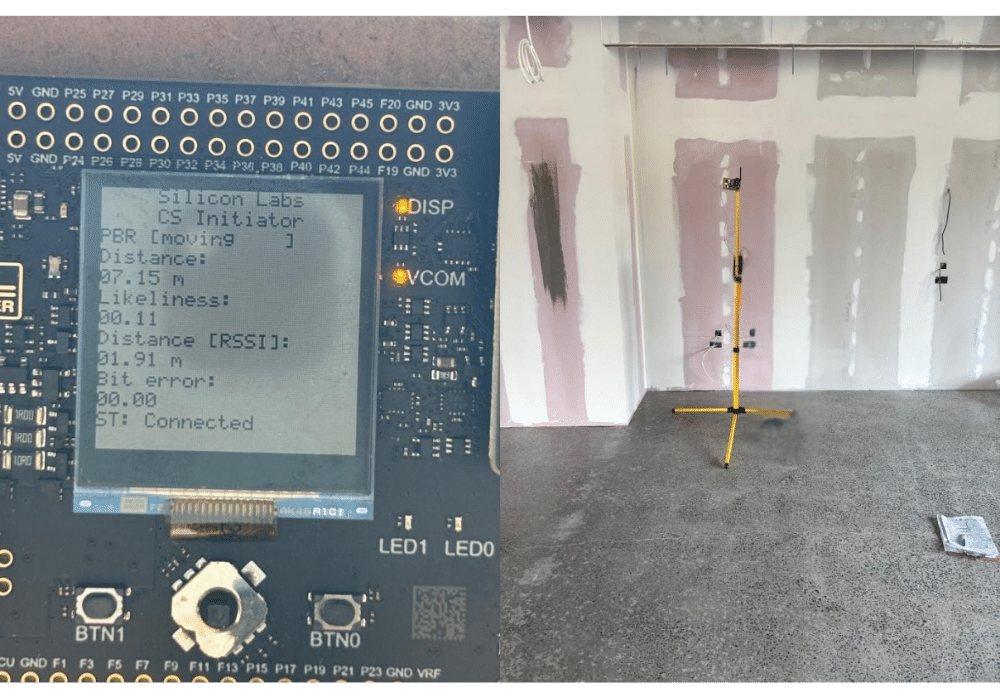
Bluetooth Channel Sounding, a capability introduced in the Bluetooth Core Specification 6.0 (finalised in September 2024), offers precise distance measurement. This technology is becoming a more established option, providing practical solutions for demanding applications.
How it works (the engineer's perspective): Channel Sounding operates by exchanging carefully timed signals across multiple radio frequencies between two BLE devices. By analysing minute phase shifts (Phase-Based Ranging - PBR) and the exact time it takes for a signal to complete a round trip (Round-Trip Time - RTT), we can determine the distance between them. The benefit of this approach is that RTT can verify PBR measurements, offering a robust defence against signal spoofing or relay attacks – an important consideration when tracking valuable assets.
- Antenna Considerations: Channel Sounding can operate with a single antenna on each communicating device, making implementation potentially simpler for tags. However, its accuracy and robustness can be further improved by using multiple antennas (up to four in the current specification) on one or both devices.
- Good Accuracy: For modular office partitions, knowing their location within a storage facility, assembly area, or even a specific section of a disassembled workspace is important. Channel Sounding can achieve accuracy typically in the range of 10-30 cm. This precision is beneficial for efficient inventory management, helping to ensure specific panels, doors, or framing elements are located promptly.
- Enhanced Security & Integrity: The combined PBR and RTT methods provide strong protection against unauthorised tracking or manipulation of location data. This helps to mitigate the spoofing of an actual component's location, ensuring that the reported position accurately reflects the physical whereabouts of the item. This means you can have confidence in the reported location of your partition components, reducing the risk of loss or misplacement and supporting the integrity of your material passport data.
- Optimised Space Utilisation: With precise distance data, you can organise storage layouts for disassembled partitions more effectively, knowing where each component is. This contributes to more efficient warehouse or staging area management, a key aspect of circularity and supports accurate inventory records for your database.
- Cost-Effective and Power Efficient: Integrating Channel Sounding into existing BLE-enabled components or adding small tags is a cost-effective and energy-efficient approach. This supports the long lifespan expected of circular economy products, helping to minimise maintenance and battery replacement needs for the tracking tags themselves.
- Robust in Complex Environments: Office buildings, even when stripped down, can present challenging radio frequency environments with reflections. Channel Sounding's algorithms are designed to mitigate multipath effects, helping to ensure reliable distance measurements for your partitions.
CTE-based Angle of Arrival (AoA): The Directional Aid for Logistics & Redeployment
Angle of Arrival (AoA), enabled by the Constant Tone Extension (CTE) in Bluetooth Core Specification 5.1 (finalised in January 2019), offers a different, but equally valuable, type of location insight: directionality.
How it works: An office partition component, equipped with a BLE tag, sends out a standard Bluetooth LE packet with a Constant Tone Extension. Specialised receiving devices, called locators, are deployed with a multi-element panel antenna. By analysing the subtle phase differences of the signal as it arrives at each antenna in the array, the locator can calculate the angle from which the signal originated. With multiple locators, you can then triangulate the position of the partition component.
Key advantages for tracking office partition components:
- Antenna Considerations: Unlike Channel Sounding, CTE-based AoA fundamentally relies on a receiver-side multi-element panel antenna array (the locator) to perform directional finding. The transmitting tag typically uses a single antenna, keeping the tag hardware simple and low-cost. For accurate angle determination, the anchor points (locators) require precise physical alignment of their antenna arrays, or the use of sophisticated correction algorithms to compensate for any phase anomalies or minor misalignments in the antennae elements.
- Directional Guidance: For large-scale projects involving the redeployment of numerous partition components, knowing not just "where" a component is, but "which direction" to go to find it, can be very helpful. Imagine a technician with a handheld device being guided directly to the correct "stack of 2.4-metre sound-dampening panels" within a large storage area. This can streamline logistics and reduce search times, directly supporting the efficient retrieval of components based on their metadata.
- Sub-metre Positioning for Larger Areas: AoA solutions typically achieve sub-metre accuracy (around 0.1-0.5 metres). This level of precision is generally adequate for room-level or specific bay-level location of partition components, particularly when considering the volume of parts in large commercial projects, and links to their material passport information for quick identification.
- Efficient Redeployment: AoA can guide teams to the location where components are needed on-site, helping to minimise wasted time and effort during installation and aiming to ensure the correct component is used in the right place, potentially preventing errors. This is vital for maximising reuse cycles.
- Scalability for Large Projects: AoA systems are suitable for tracking a good number of tags simultaneously. This is crucial for managing thousands of individual partition components across multiple floors or even multiple building projects, feeding real-time location data into your centralised component database.
- Streamlined Deconstruction Planning: When it comes to deconstructing existing office spaces for component reuse, AoA can provide a clear, real-time map of where components are, assisting in efficient removal and categorisation for their next life – all of which can be precisely logged in the metadata database linked to each component's DPP.
Full Stack Energy's Strategic Approach
For customers looking to enhance resource management and operational efficiency, the optimal solution often involves a strategic integration of both Bluetooth Channel Sounding and CTE-based AoA.
- For detailed inventory management, secure storage, and precise tracking of individual, higher-value items within a defined area (e.g., specific acoustic panels in a workshop, or critical tools in a confined storage zone), Bluetooth Channel Sounding is a strong option. Its accuracy helps ensure every item is accounted for and easily retrieved, supporting the precision needed for comprehensive metadata and digital passports.
- For large-scale logistics, efficient asset flow across broader spaces, directional guidance for personnel, or real-time visibility in dynamic environments (e.g., tracking office partition components for redeployment, navigating through a warehouse, or monitoring equipment in a large facility), CTE-based AoA provides a valuable layer of intelligence. It transitions from "finding" to "being guided," potentially improving operational efficiency by making it easier to locate assets or even people based on their unique tag ID and associated data.
By selectively deploying these advanced BLE technologies, Full Stack Energy can support a wide range of applications. This encompasses not only circular economy models for building components and refined logistics, but also extends to optimising general warehouse operations, enhancing safety through people and asset tracking, and a multitude of other industrial use cases beyond typical logistics. Ultimately, it's about enabling a more sustainable, efficient, and profitable future for diverse industries, driven by the increasing necessity of material passports and comprehensive metadata for valuable assets.









