As EV charging has grown and become commonplace, so has a collection of standards and protocols. These standards and protocols serve EV owners, fleet managers, EVSE manufacturers, CPMS developers, CPOs and EMSPs. Standards and protocols reduce development costs, enabling growth through interoperability and establishing a fully functioning market for Electric Vehicle operations.

OCPP
Open Charge Point ProtocolThe Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) was developed by the Open Charge Alliance (OCA), facilitating communication between electric vehicle charging stations and their respective central management systems. The protocol cuts costs and reduces the risk of networked infrastructure investments. Furthermore, it offers operators plenty of flexibility when selecting EVSE models and simple access for electric vehicle drivers.
For manufacturers of charging equipment, software providers, network operators and research organisations alike, OCPP has quickly become the industry standard for EV infrastructure interoperability.
Over the years, EV industry players - such as charging station manufacturers, utility companies, charge point operators and back-office software providers - have collaborated to develop OCPP 1.6: a protocol that provides smart charging capability while maintaining high levels of security. Most of today's implementations are based on this version of the standard.
OCPP 2.0 has improved device management, transaction handling, security measures and smart charging capabilities with a host of new features designed to enhance the EV charging experience for users. Furthermore, this version offers plug-and-charge support for electric vehicles compatible with ISO 15118 protocol - ensuring you have all the tools necessary to charge your vehicle quickly and safely seamlessly!
OSCP
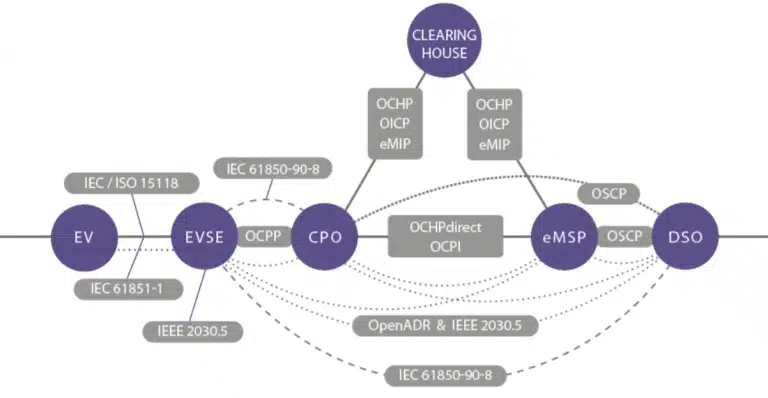
Open Smart Charging ProtocolThe Open Smart Charging Protocol (OSCP) 1.0 is a standard for communication between charge point management systems (CPMS) and energy management systems (EMS) of site owners or distribution system operators (DSO). OSCP facilitates capacity-based smart charging of EVs by enabling the real-time prediction of the local electricity grid capacity to be communicated to the charge point operator.
It enables charge points to optimise their power output accordingly, resulting in lower energy costs and fewer peak loads. In addition, this protocol also supports remote access and control of EVSEs from a central location, giving operators greater visibility into their operations.
OCPI
Open Charge Point InterfaceThe Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) is an international protocol developed to enable e-mobility services providers, charge point operators (CPOs), and energy management service providers (EMSP) to securely exchange data for electric vehicle charging services. This standardised data exchange covers charge point locations, pricing information, real-time billing, mobile access and more. It defines the formats of messages sent between different parts of the network - such as the user's smartphone app and the central back office systems.
OCPI has quickly become a powerful tool in connecting EV infrastructure platforms across Europe. By using OCPI standards, companies can develop their APIs that enable interoperability between CPMS and CPO/EMSP, allowing them to easily share data securely and cost-effectively. Additionally, this protocol introduces visibility into the e-mobility market and creates an open environment for businesses to thrive.
In summary, OCPI and OCPP are two essential standards in electric vehicle charging. They enable interoperability between EV infrastructure providers, enable smart charging capabilities and allow for seamless transactions between users and operators. With these protocols continuing to evolve, it is no surprise that they have become essential tools for anyone involved with electrifying transportation.
The benefits of using these standards are clear - from reduced costs to increased efficiency. Understanding their features and capabilities ensures your organisation has the foundation for its EV operations.
OCPI V2.2 Supported Features
- Roaming via hub
- Roaming peer-2-peer
- Roaming with mixed roles
- Authorization
- Reservation
- Provide tariff information
- Billing
- Provide static charge point information (e.g. location)
- Provide real-time charge point status information
- Provide (real-time) session information
- Provide CDR information
- Remote start/stop (for use via mobile app)
- Smart charging support
- Platform monitoring
OpenADR
Open Automated Demand ResponseOpen Automated Demand Response (OpenADR) is the leading communication infrastructure for automated demand response. OpenADR was developed to provide an open and secure foundation for interoperable information exchange that facilitates demand response programs. It is typically used to send signals from utilities, distribution system operators (DSO), or other wholesale market participants to energy management and control systems to balance energy demand during peak times.
OpenADR is an international standard developed by the Open Smart Grid Protocol (OSGP) Alliance. It enables secure communication between utility or distribution system operators and their customers, leading to more efficient utilization of electricity resources. Its flexibility makes it well-suited for various use cases, including time-of-use pricing, demand response programs, and other smart grid applications.
OpenADR provides an open platform for two-way communication between energy suppliers and customers. It enables automated communications for price signals, load-shedding events, real-time pricing information, renewable energy integration requests, emergency notifications and more.
ISO 15118
ISO 15118 is an international standard defining the communication protocols between an EV and an electric vehicle charging station.
The standard can be used for both wired (AC and DC charging) and wireless charging for electric vehicles. The standard incorporates the Plug & Charge feature used by some electric vehicle networks. Plug and Charge enables an EV to automatically identify and authorise itself to a charging station on behalf of the driver to receive energy for recharging its battery. The only action the driver requires is to plug the charging cable into the EV or charging station. This process is enabled by a digital certificate located in the vehicle, allowing it to communicate with the charging point management system (CPMS). This enables a seamless end-to-end charging process, which includes automatic authentication and billing, and avoids the need to use an RFID card, an app or to memorise PIN numbers.
ISO 15118 also enables bi-directional EV charging, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G). With V2G, electric vehicles can feed energy back to the grid when needed, thus helping reduce costly system peaks and ensuring a more intelligent, reliable grid.









